Advanced Example
Complete example demonstrating reading data, slicing an EISCube, fitting the spectra, extracting the profile at the coordinates of maximum intensity, and finally making a nice overview plot.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import astropy.units as u
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord
from astropy.wcs.utils import wcs_to_celestial_frame
import eispac
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Read in the fit template and EIS observation
data_filepath = './eis_20190404_131513.data.h5'
template_filepath = './fe_12_195_119.2c.template.h5'
tmplt = eispac.read_template(template_filepath)
data_cube = eispac.read_cube(data_filepath, tmplt.central_wave)
# Select a cutout of the raster
eis_frame = wcs_to_celestial_frame(data_cube.wcs)
lower_left = [None, SkyCoord(Tx=-25, Ty=225, unit=u.arcsec, frame=eis_frame)]
upper_right = [None, SkyCoord(Tx=175, Ty=425, unit=u.arcsec, frame=eis_frame)]
raster_cutout = data_cube.crop(lower_left, upper_right)
# Fit the data and save it to disk
fit_res = eispac.fit_spectra(raster_cutout, tmplt, ncpu='max')
save_filepaths = eispac.save_fit(fit_res, save_dir='cwd')
# Find indices and world coordinates of max intensity
sum_data_inten = raster_cutout.sum_spectra().data
iy, ix = np.unravel_index(sum_data_inten.argmax(), sum_data_inten.shape)
ex_world_coords = raster_cutout.wcs.array_index_to_world(iy, ix, 0)[1]
y_arcsec, x_arcsec = ex_world_coords.Ty.value, ex_world_coords.Tx.value
# Extract data profile and interpolate fit at higher spectral resolution
data_x = raster_cutout.wavelength[iy, ix, :]
data_y = raster_cutout.data[iy, ix, :]
data_err = raster_cutout.uncertainty.array[iy, ix, :]
fit_x, fit_y = fit_res.get_fit_profile(coords=[iy,ix], num_wavelengths=100)
c0_x, c0_y = fit_res.get_fit_profile(0, coords=[iy,ix], num_wavelengths=100)
c1_x, c1_y = fit_res.get_fit_profile(1, coords=[iy,ix], num_wavelengths=100)
c2_x, c2_y = fit_res.get_fit_profile(2, coords=[iy,ix], num_wavelengths=100)
# Make a multi-panel figure with the cutout and example profile
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[10,5])
plot_grid = fig.add_gridspec(nrows=1, ncols=2, wspace=0.3)
data_subplt = fig.add_subplot(plot_grid[0,0])
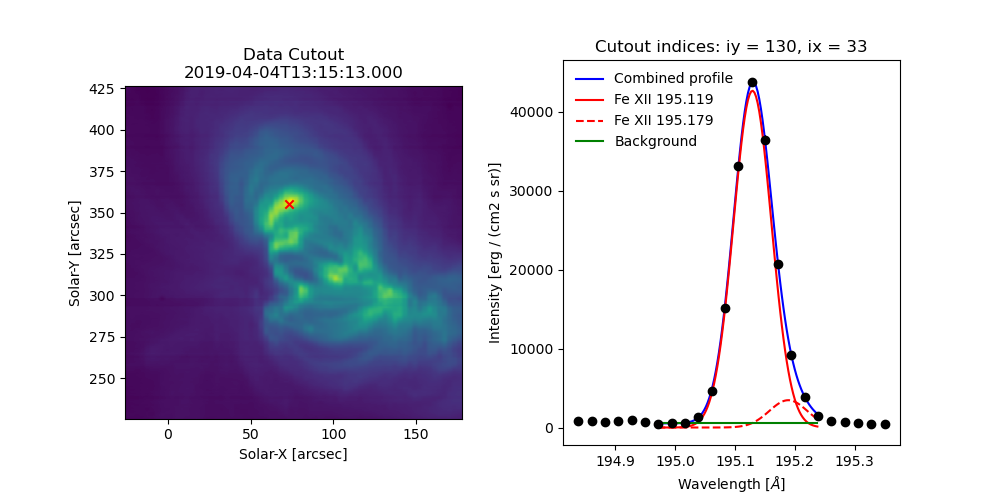
data_subplt.imshow(sum_data_inten, origin='lower', extent=cutout_extent)
data_subplt.scatter(x_arcsec, y_arcsec, color='r', marker='x')
data_subplt.set_title('Data Cutout\n'+raster_cutout.meta['mod_index']['date_obs'])
data_subplt.set_xlabel('Solar-X [arcsec]')
data_subplt.set_ylabel('Solar-Y [arcsec]')
profile_subplt = fig.add_subplot(plot_grid[0,1])
profile_subplt.errorbar(data_x, data_y, yerr=data_err, ls='', marker='o', color='k')
profile_subplt.plot(fit_x, fit_y, color='b', label='Combined profile')
profile_subplt.plot(c0_x, c0_y, color='r', label=fit_res.fit['line_ids'][0])
profile_subplt.plot(c1_x, c1_y, color='r', ls='--', label=fit_res.fit['line_ids'][1])
profile_subplt.plot(c2_x, c2_y, color='g', label='Background')
profile_subplt.set_title(f'Cutout indices: iy = {iy}, ix = {ix}')
profile_subplt.set_xlabel('Wavelength [$\AA$]')
profile_subplt.set_ylabel('Intensity ['+raster_cutout.unit.to_string()+']')
profile_subplt.legend(loc='upper left', frameon=False)
plt.show()